
Xenon oxygen compounds
 المؤلف:
Peter Atkins, Tina Overton, Jonathan Rourke, Mark Weller, and Fraser Armstrong
المؤلف:
Peter Atkins, Tina Overton, Jonathan Rourke, Mark Weller, and Fraser Armstrong
 المصدر:
Shriver and Atkins Inorganic Chemistry ,5th E
المصدر:
Shriver and Atkins Inorganic Chemistry ,5th E
 الجزء والصفحة:
ص444-445
الجزء والصفحة:
ص444-445
 2025-09-22
2025-09-22
 321
321
Xenon oxygen compounds
Key point: The xenon oxides are unstable and highly explosive. Xenon oxides are endergonic (ΔfGO>0) and cannot be pre pared by direct interaction of the elements. The oxides and oxo fluorides are prepared by the hydrolysis of xenon fluorides:
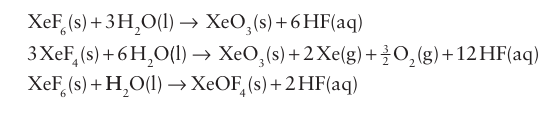
The pyramidal xenon trioxide, XeO3(4) presents a serious hazard because this endergonic compound is highly explosive. It is a very strong oxidizing agent in acidic solution, with E ْ (XeO3, Xe) +=2.10 V. In basic aqueous solution the Xe (VI) oxoanion HXeO4 slowly decomposes in a coupled disproportionation and water oxidation to yield a Xe (VIII) perxenate ion, XeO6-4, and xenon:
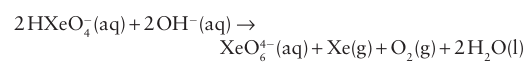
The perxenates of several alkali metal ions have been prepared by treatment of XeO3 with ozone in basic conditions. These compounds are white crystalline solids with octahedral XeO6 4 units (12). They are powerful oxidizing agents in acidic aqueous solution:
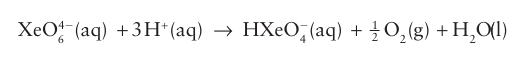
Treating Ba2XeO6 with concentrated sulfuric acid produces the only other known oxide of xenon, XeO4 (5), which is an explosively unstable gas.
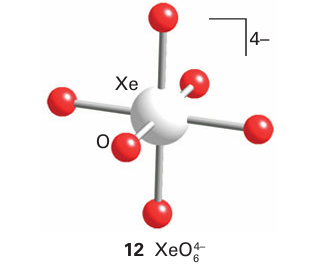
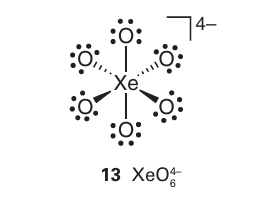
A brief illustration. Thestructure of many xenon compounds can be successfully predicted by using the VSEPR model. The Lewis structure of the perxenate ion is shown in (13). With six electron pairs around the Xe atom, the VSEPR model predicts an octahedral arrangement of bonding electron pairs and an octahedral overall structure.
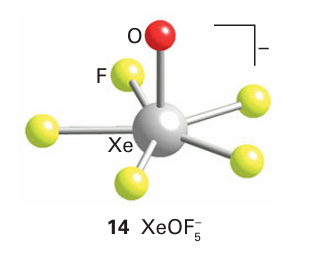
Xenon forms the oxofluorides XeOF2(6), XeO3F2 (7), and XeOF4 (8). When alkali metal fluorides are dissolved in XeOF4, solvated fluoride ions are formed of composition F-.3XeOF4. Attempted removal of XeOF4 from the solvate yields XeOF5 (14), which is a pentagonal pyramid.
A brief illustration. Thestructures of compounds of xenon can be probed using 129Xe-NMR spectroscopy. For example, the 129Xe-NMR spectrum of XeOF4 (8) consists of a quintuplet of peaks. These peaks correspond to the single Xe environment, which is coupled to four equivalent 19F atoms.

 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


