
Synthesis and structure of xenon fluorides
 المؤلف:
Peter Atkins, Tina Overton, Jonathan Rourke, Mark Weller, and Fraser Armstrong
المؤلف:
Peter Atkins, Tina Overton, Jonathan Rourke, Mark Weller, and Fraser Armstrong
 المصدر:
Shriver and Atkins Inorganic Chemistry ,5th E
المصدر:
Shriver and Atkins Inorganic Chemistry ,5th E
 الجزء والصفحة:
ص442-443
الجزء والصفحة:
ص442-443
 2025-09-22
2025-09-22
 348
348
Synthesis and structure of xenon fluorides
Key point: Xenon reacts with fluorine to form XeF2, XeF4, and XeF6. The reactivity of the noble gases has been investigated sporadically ever since their discovery, but all early attempts to coerce them into compound formation were unsuccessful. Until the 1960s the only known compounds were the unstable diatomic species such as He2 and Ar2, which were detected only spectroscopically. However, in March 1962, Neil Bartlett, then at the University of British Columbia, observed the reaction
of a noble gas. Bartlett’s report, and another from Rudolf Hoppe’s group in the University of Munster a few weeks later, set off a flurry of activity throughout the world. Within a year, a series of xenon fluorides and oxo compounds had been syn thesized and characterized. The field is somewhat limited, but compounds with bonds to nitrogen, carbon, and metals have been prepared. Bartlett’s motivation for studying xenon was based on the observations that PtF6 can oxidize O2, to give the solid O2 PtF6, and that the ionization energy of xenon is similar to that of molecular oxygen. Indeed, reaction of xenon with PtF6 did give a solid, but the reaction is complex and the complete formulation of the product (or products) remains unclear. The direct reaction of xenon and fluorine leads to a series of compounds with oxidation numbers +2 (XeF2), +4 (XeF4), and +6 (XeF6). The structures of XeF2 and XeF4 are well-established from diffraction and spectroscopic methods. Similar measurements on XeF6 in the gas phase, however, led to the conclusion that this molecule is fluxional. Infrared spectra and electron diffraction on XeF6 show that a distortion occurs about a threefold axis, suggesting that a triangular face of F atoms opens up to accommodate a lone pair of electrons, as in (3). One interpretation is that the fluxional process arises from the migration of the lone pair from one triangular face to another. Solid XeF6 consists of F-bridged XeF5 units and in solution it forms Xe4F24 tetramers. The gaseous and solid structures bear a molecular and electronic structural resemblance to the isoelectronic polyhalide anions I3 and ClF4 (Section 17.10c).
The xenon fluorides are synthesized by direct reaction of the ele ments, usually in a nickel reaction vessel that has been passivated by exposure to F2 to form a thin protective NiF2 coating. This treatment also removes surface oxide, which would react with the xenon fluorides. The synthetic conditions indicated in the follow ing equations show that formation of the higher halides is favoured by a higher proportion of fluorine and higher total pressure:
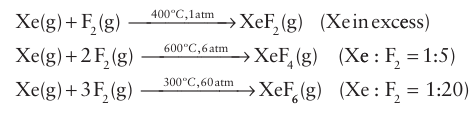
A simple ‘window-sill’ synthesis is also possible. Xenon and fluorine are sealed in a glass bulb (rigorously dried to prevent the formation of HF and the attendant etching of the glass) and the bulb is exposed to sunlight, whereupon beautiful crystals of XeF2 slowly form in the bulb. It will be recalled that F2 undergoes photodissociation, and in this synthesis the photo chemically generated F atoms react with Xe atoms.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


