
Properties of Alcohols and Phenols : The effect of van der Waals forces
 المؤلف:
..................
المؤلف:
..................
 المصدر:
LibreTexts Project
المصدر:
LibreTexts Project
 الجزء والصفحة:
.................
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
 4-9-2019
4-9-2019
 1291
1291
The effect of van der Waals forces
- Boiling points of the alcohols: Hydrogen bonding is not the only intermolecular force alcohols experience. There are also van der Waals dispersion forces and dipole-dipole interactions. The hydrogen bonding and dipole-dipole interactions are much the same for all alcohols, but dispersion forces increase as the alcohols get bigger. These attractions get stronger as the molecules get longer and have more electrons. This increases the sizes of the temporary dipoles formed. This is why the boiling points increase as the number of carbon atoms in the chains increases. It takes more energy to overcome the dispersion forces, and thus the boiling points rise.
- Comparison between alkanes and alcohols: Even without any hydrogen bonding or dipole-dipole interactions, the boiling point of the alcohol would be higher than the corresponding alkane with the same number of carbon atoms.
Compare ethane and ethanol:
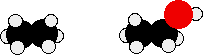
Ethanol is a longer molecule, and the oxygen atom brings with it an extra 8 electrons. Both of these increase the size of the van der Waals dispersion forces, and subsequently the boiling point. A more accurate measurement of the effect of the hydrogen bonding on boiling point would be a comparison of ethanol with propane rather than ethane. The lengths of the two molecules are more similar, and the number of electrons is exactly the same.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


