


 6:34:19
6:34:19  2019-11-04
2019-11-04  1184
1184
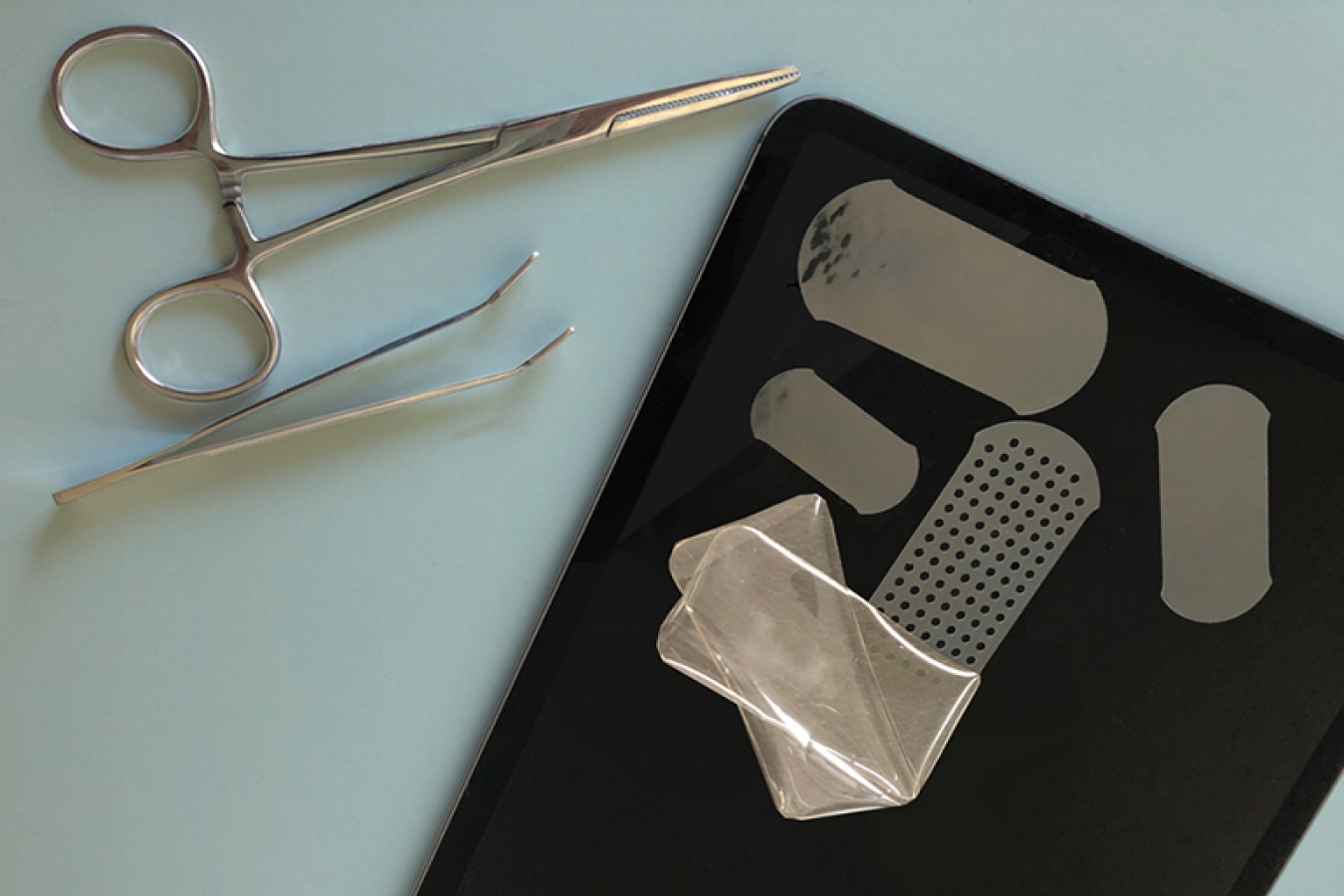
Researchers at MIT have developed an adhesive tape that can quickly seal wounds and bind tissues together, potentially even binding implantable medical devices to a target site. The researchers hope that the tape could eventually replace surgical sutures, which have a variety of limitations.
“There are over 230 million major surgeries all around the world per year, and many of them require sutures to close the wound, which can actually cause stress on the tissues and can cause infections, pain, and scars,” said Xuanhe Zhao, one of the researchers involved in the study. “We are proposing a fundamentally different approach to sealing tissue.”
Sticking two wet tissue surfaces together is challenging. Sutures are not always suitable, particularly for soft and fragile tissues such as the lungs. Surgeons currently use surgical glues as an alternative, but these can sometimes take several minutes to adhere, and can spread or drip onto tissues where they are not wanted.
These researchers were inspired by the sticky materials that spiders use to trap insects. Such materials are sticky even under wet conditions because of the presence of charged polysaccharides that rapidly draw moisture away from a surface, drying a small piece of it and allowing a glue to stick.
The new tape relies on polyacrylic acid to absorb water from a tissue surface and form a temporary bond. Then, compounds called NHS esters in the tape form much stronger bonds with tissue proteins. Strikingly, the entire process of sticking takes only five seconds.
By changing the ratio of rapidly and slowly degrading components, the researchers were able to make the tape provide short- or long-term adhesion, and the correct type of tape can be used for a particular application. Interestingly, the tape is also useful for adhering implantable medical devices. For instance, the researchers were able to stick a patch onto rat hearts using the adhesive tape.
“This provides a more elegant, more straightforward, and more universally applicable way of introducing an implantable monitor or drug delivery device, because we can adhere to many different sites without causing damage or secondary complications from puncturing tissue to affix the devices,” said Hyunwoo Yuk, another researcher involved in the study.
Reality Of Islam |
|
A newly dev

Get ready f

Researchers

A new metas
 9:3:43
9:3:43
 2018-11-05
2018-11-05
10 benefits of Marriage in Islam
 7:5:22
7:5:22
 2019-04-08
2019-04-08
benefits of reciting surat yunus, hud &
 9:45:7
9:45:7
 2018-12-24
2018-12-24
advantages & disadvantages of divorce
 11:35:12
11:35:12
 2018-06-10
2018-06-10
 6:0:51
6:0:51
 2018-10-16
2018-10-16
 8:19:41
8:19:41
 2018-06-21
2018-06-21
 1:34:8
1:34:8
 2022-02-01
2022-02-01
 8:15:37
8:15:37
 2023-02-16
2023-02-16
 11:11:59
11:11:59
 2023-02-01
2023-02-01
 5:58:12
5:58:12
 2021-12-18
2021-12-18
 7:26:19
7:26:19
 2022-04-08
2022-04-08
 7:6:7
7:6:7
 2022-03-21
2022-03-21
 5:41:46
5:41:46
 2023-03-18
2023-03-18
| LATEST |