


 5:30:36
5:30:36  2019-08-15
2019-08-15  1094
1094
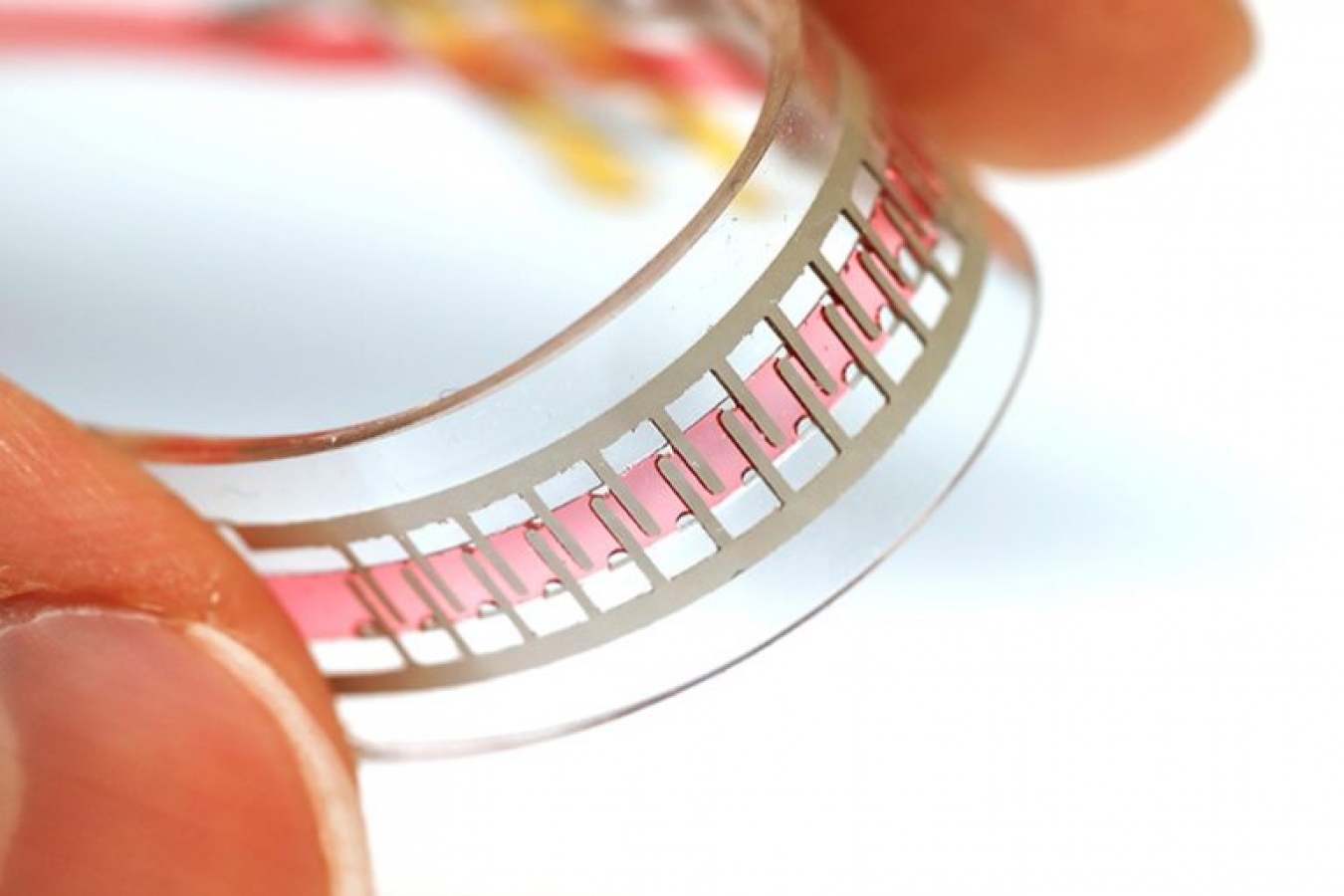

Researchers at Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne in Switzerland have developed a flexible and stretchable pump for soft robotics. The existence of the device, described in the latest journal Nature, means that soft robots may no longer need to be tethered to rigid and bulky pumps, allowing for greater versatility in soft medical devices, such as artificial muscles and assistive wearables.
Soft robots offer significant advantages in medical devices, as they can more safely interact with human tissues without causing damage. Possibilities range from soft assistive devices to help those with impaired mobility, to artificial muscles and surgical devices.
Typically, such robots require actuation, where a pump forces liquid or air into parts of the robot to make it move in a certain way. However, current pumps are often rigid and bulky, meaning that they are tethered to the robot by a tube, and such robots are limited in where and how they can move.
The Swiss-based researchers have developed a completely soft pump, meaning that the new pump could be an on-board component in a soft robot. The new pump is flexible and stretchable, weighs just 1 gram, contains soft electrodes, and uses very little power.
A method used to circulate cooling liquid inside supercomputers provided the inspiration for the pump design. In the center of the pump a 1 mm channel contains numerous printed electrodes, which are bathed in a dielectric liquid. Applying a voltage to the electrodes causes the fluid to be pulled through the pump.
The flexible pumps can be directly integrated into soft robots, meaning that if they have an on-board power supply, they could be tetherless. “If we want to actuate larger robots, we connect several pumps together,” said Herbert Shea, a researcher involved in the study. “We consider this a paradigm shift in the field of soft robotics.”
The researchers are working with a Japanese research group to integrate the pump into flexible artificial muscles and soft exoskeletons.
Source: Medgadget
Reality Of Islam |
|
A newly dev

Get ready f

Researchers

A new metas
 9:3:43
9:3:43
 2018-11-05
2018-11-05
10 benefits of Marriage in Islam
 7:5:22
7:5:22
 2019-04-08
2019-04-08
benefits of reciting surat yunus, hud &
 9:45:7
9:45:7
 2018-12-24
2018-12-24
advantages & disadvantages of divorce
 11:35:12
11:35:12
 2018-06-10
2018-06-10
 6:0:51
6:0:51
 2018-10-16
2018-10-16
the happy life of mankind requirement
 6:36:36
6:36:36
 2022-01-25
2022-01-25
 2:42:26
2:42:26
 2023-02-02
2023-02-02
 9:39:36
9:39:36
 2022-12-28
2022-12-28
 5:58:12
5:58:12
 2021-12-18
2021-12-18
 2:11:12
2:11:12
 2022-10-15
2022-10-15
bahlool & the throne of haroun rashid
 8:20:35
8:20:35
 2018-06-21
2018-06-21
 10:43:56
10:43:56
 2022-06-22
2022-06-22
 5:41:46
5:41:46
 2023-03-18
2023-03-18
| LATEST |