
The overlap Integral
 المؤلف:
Peter Atkins، Julio de Paula
المؤلف:
Peter Atkins، Julio de Paula
 المصدر:
ATKINS PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
المصدر:
ATKINS PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
 الجزء والصفحة:
375
الجزء والصفحة:
375
 2025-11-27
2025-11-27
 57
57
The overlap integral
The extent to which two atomic orbitals on different atoms overlap is measured by the overlap integral, S:
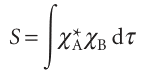
If the atomic orbital χA on A is small wherever the orbital χB on B is large, or vice versa, then the product of their amplitudes is everywhere small and the integral—the sum of these products—is small (Fig. 11.28). If χA and χB are simultaneously large in some region of space, then S may be large. If the two normalized atomic orbitals are identical (for instance, 1s orbitals on the same nucleus), then S = 1. In some cases, simple formulas can be given for overlap integrals and the variation of S with bond length plotted (Fig. 11.29). It follows that S = 0.59 for two H1s orbitals at the equilibrium bond length in H2 +, which is an unusually large value. Typical values for orbitals with n=2 are in the range 0.2 to 0.3. Now consider the arrangement in which an s orbital is superimposed on a px orbital of a different atom (Fig. 11.30). The integral over the region where the product of orbitals is positive exactly cancels the integral over the region where the product of orbitals is negative, so overall S = 0 exactly. Therefore, there is no net overlap between the s and porbitals in this arrangement.
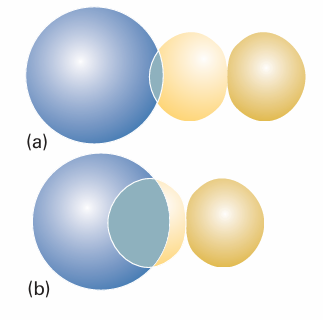
Fig. 11.28 (a) When two orbitals are on atoms that are far apart, the wavefunctions are small where they overlap, so S is small. (b) When the atoms are closer, both orbitals have significant amplitudes where they overlap, and S may approach 1. Note that S will decrease again as the two atoms approach more closely than shown here, because the region of negative amplitude of the p orbital starts to overlap the positive overlap of the s orbital. When the centres of the atoms coincide, S = 0.

Fig. 11.29 The overlap integral, S, between two H1s orbitals as a function of their separation R.
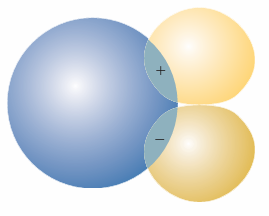
Fig. 11.30 A p orbital in the orientation shown here has zero net overlap (S = 0) with the s orbital at all internuclear separations.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


