
Research methodology
 المؤلف:
Peter Donnan & Christine Brown & Gwyn Brickell
المؤلف:
Peter Donnan & Christine Brown & Gwyn Brickell
 المصدر:
Enhancing Teaching and Learning through Assessment
المصدر:
Enhancing Teaching and Learning through Assessment
 الجزء والصفحة:
P434-C36
الجزء والصفحة:
P434-C36
 2025-08-16
2025-08-16
 598
598
Research methodology
This qualitative study, to be written up as a series of multiple cases, will be based on data collection from three rounds of semi-structured interviews conducted with the participants at six month intervals. Educational developers' perspectives about assessment are best expressed in their individual voices because there are significant differences in the institutional contexts of Australian universities; furthermore, the experience and perceptions of each developer are unique.
The first interview series focused on participants' backgrounds, approaches and professional orientations towards assessment that was beginning to incorporate online elements; the second interview series targeted responses to a range of e-assessments categories derived from the literature, as well as seeking responses to a framework developed from the first round; the final round of interviews will take up issues explored as well as returning to ongoing influences and critical events that are impacting on participants' thinking about assessment in online environments.
The broad categories and focus of questions for the series of three interviews are presented in the following table. The questions in rounds 2 and 3 were evolved in response to themes and responses emerging from the previous round so that there is a cyclical pattern to the study.
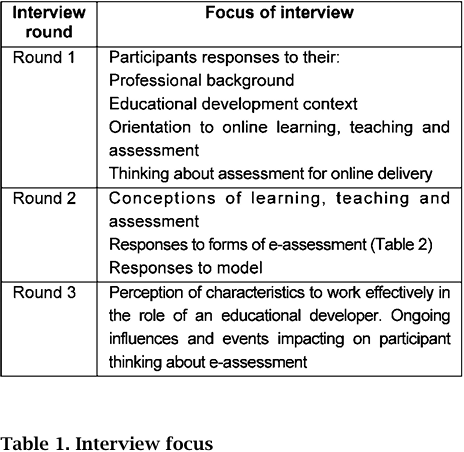
We draw only upon the first two rounds of interviews but it explores emerging issues that are pertinent to the final round.
An interpretive analysis of the transcripts using NVivo informs the discussion and findings.
As part of the methodology a spectrum of types of e assessment, presented in Table 2, was derived from the literature and participants were invited to comment on various issues arising from the table as well as to suggest refinements. The rationale was to explore participants' thinking about assessment across a spectrum of types of e-assessment. Some reporting and analysis of participant comments on the categories in Table 2 are presented in the following section on Results, analysis and discussions. The fact that Table 2 is entitled Forms of E-assessment is not an assumption that with online delivery a new category of assessment is created. What is being explored is the thinking about assessment when there is an intersection of pedagogy and technology in online environments.
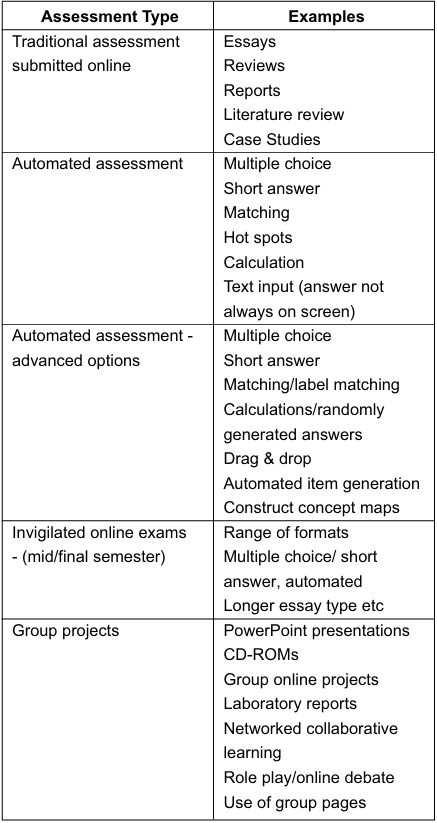
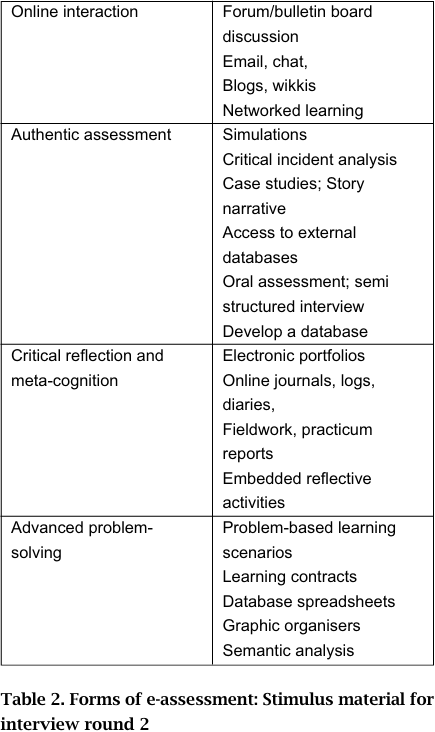
As one explores the categories in this table it becomes obvious that there are relativities with some of the options in terms of the sophistication levels of technology skills and support that one has available to implement various forms of e-assessment. An individual academic would find it difficult for example to construct complex problem-based learning scenarios using a range of multi-media to enrich the presentation problem etc. It would be different of course if that academic was supported by a teaching grant or had ready access to technology support.
Table 2 relates broad categories of assessment to examples of assessment that may be conducted online. The advantages of web-based assessment have been widely recognized. Zhang, Khan, Gibbons and Ni (2002) typically highlight the fact that it can reach a large population; it is time, place and platform independent, with simple update procedures; and it offers enhanced opportunities to collect and analyze feedback. They also add that web-based assessment tools support different media such as plain text, rich text format, still image, video and audio in representing assessment items. O'Reilly (2001) also notes the easy links to real data, the availability of expert help, possibility of rapid feedback, archival options of all interactions, more time for preparation of assignments with online submissions and the human-human interaction, as well as human-computer interaction in relation to online assessment. What is being recognized by these authors are the learning affordances that the technology offers.
The term affordances, originally used in environmental psychology, is now being adopted to extend the potential of the technology in e-learning, to pursue the educational uses it invites and facilitates (Conole & Dyke, 2004) or simply to use the potential of the design elements. Dabbagh and Bannan-Ritland (2005) recognize the undoubted potential of online learning for socially mediated and more globally focused learning and in these senses the concept of 'affordances' could constitute an important dimension in the thinking about e-assessment.
 الاكثر قراءة في Teaching Strategies
الاكثر قراءة في Teaching Strategies
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


