
Exemplars Peers
 المؤلف:
Paul Lam & Paula Hodgson & Josephine Csete
المؤلف:
Paul Lam & Paula Hodgson & Josephine Csete
 المصدر:
Enhancing Teaching and Learning through Assessment
المصدر:
Enhancing Teaching and Learning through Assessment
 الجزء والصفحة:
P397-C33
الجزء والصفحة:
P397-C33
 2025-08-11
2025-08-11
 402
402
Exemplars Peers
In the present study the use of student-to-student interaction was even more prevalent than student-to-content. The following are two examples illustrating the range of methods that fall within this category.
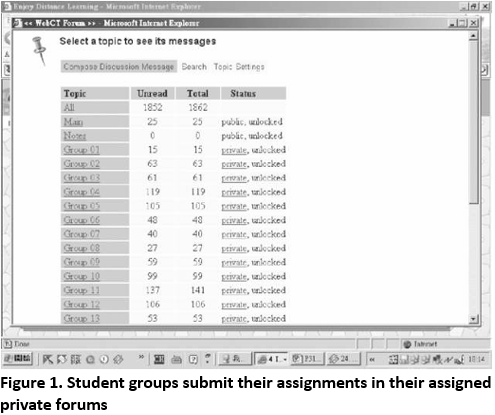
Online peer review of assignments is a good strategy to encourage students to interact and engage in focused discussions with each other. A design to enhance student-student interaction was implemented on the assignment of a course on nursing for an undergraduate program where the teacher first required her students to submit their assignments, done in groups, to their pre-assigned private forum on the course website (Figure 1); she then specified a timeline for group members to review each others' work and provide comments online. In this case, these students were taking on dual roles as authors and evaluators. Students were engaged actively in the group activity. A high level of interaction between group members was observed in the assignment discussion forums, although some group's participation levels were higher than others. Multiple contributions from peer group members facilitated a broadening of perspectives in the learning process. Furthermore, the asynchronous mode of discussion provided a better opportunity for students to reflect and learn flexibly in their own time. Ultimately, these students' skills as reflective practitioners may be enhanced.
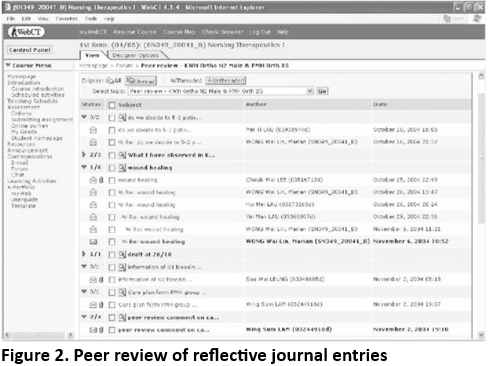
Building online journals/blogs is another way to encourage students to interact with each other. As illustrated in the previous case, developing reflective skills is important for student nurses. In the workplace, they need to communicate well with other clinical professionals and develop critical thinking skills to make sound judgments. To promote supportive peer learning in developing these skills in nursing, the students were asked to post reflective journals in an assigned online forum. They submitted their experiences and reflections of clinical practice for their peers to review and comment (Figure 2). In order to encourage the postings of journals and the provision of feedback for others' writing, grades were allocated depending on both the original journal entries posted and the quality and quantity of feedback that students provided to their peers. The majority of students were motivated in this case because the effort needed to provide good-quality feedback was recognized. Students did not perceive themselves as taking on more work, and they were appreciative of the heightened awareness of the quality of their performance. Conclusively, the assessment promoted rich student-student interactions.
Note that both of these interaction-with-peers exemplars require input from the instructors in the form of: 1) setting up the activity; 2) maintaining a "virtual presence" during the activity; and 3) providing feedback via calculations that lead to grades and/or written commentary after the completion of the activity.
 الاكثر قراءة في Teaching Strategies
الاكثر قراءة في Teaching Strategies
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


