
Peer Assessment among Students in a Problem-Based Learning Format Procedure Results
 المؤلف:
Steve Frankland
المؤلف:
Steve Frankland
 المصدر:
Enhancing Teaching and Learning through Assessment
المصدر:
Enhancing Teaching and Learning through Assessment
 الجزء والصفحة:
P150-C14
الجزء والصفحة:
P150-C14
 2025-06-28
2025-06-28
 575
575
Peer Assessment among Students in a Problem-Based Learning Format Procedure Results
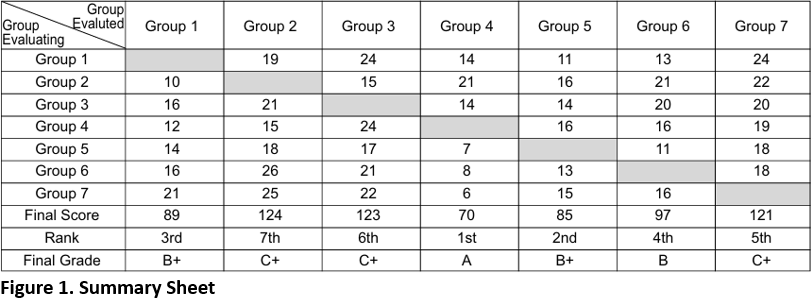
Using the results of the numerical scores, with seven groups in the class, each group would evaluate the six other groups, so the best-case scenario would be if a particular group was ranked 1st on each occasion for each of the five criteria, i.e. 1st x 5 factors x 6 groups = a total score of 30. Conversely, worst case scenario would be if a particular group was ranked 6th (last) on each occasion for each of the five criteria, i.e. 6th x 5 factors x 6 groups = a total score of 180. Accordingly, a score of each group will range between 30 (1st for every factor by each group) and 180 (last on each factor by each group).
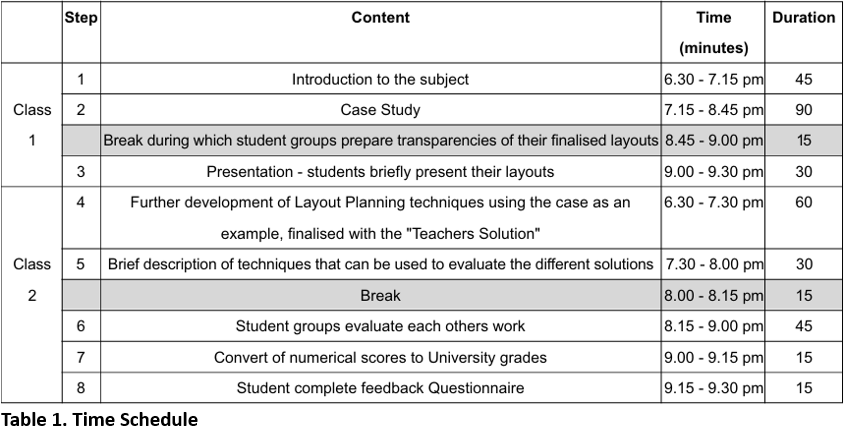
Finally, the numerical scores were converted to the University's grading system. i.e. A+ (Outstanding), A (Excellent) B+ (Very Good), B (Good), C+ (Wholly Satisfactory), C (Satisfactory), D+ (Barely Adequate) D (Weak) and F (Fail). This was done by the teacher who used subjective judgement by looking for natural breaks between the relative scores of groups. This is shown on the Evaluation sheet in Figure 3 in Peer Assessment among Students in a Problem-Based Learning Format Procedure.
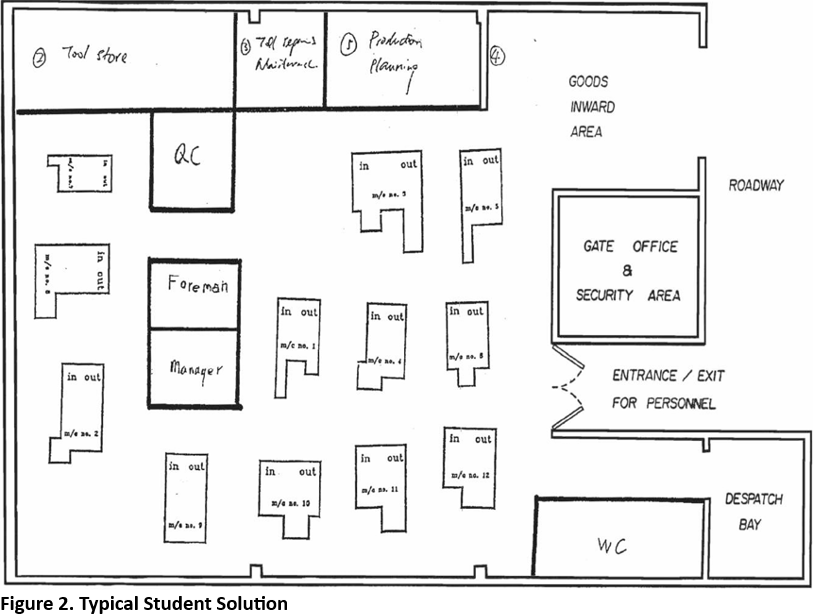
Within these two classes, students were introduced to various practical payout planning and evaluation techniques used in engineering, as well as other forms of management. A learning environment was created that allowed students to act as a group of engineers working together to solve a realistic problem. Without strong intervention from the teacher, this case provokes students to discuss and share ideas, identify priorities, and examine the materials in the limited time available.
 الاكثر قراءة في Teaching Strategies
الاكثر قراءة في Teaching Strategies
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


