

Grammar


Tenses


Present

Present Simple

Present Continuous

Present Perfect

Present Perfect Continuous


Past

Past Simple

Past Continuous

Past Perfect

Past Perfect Continuous


Future

Future Simple

Future Continuous

Future Perfect

Future Perfect Continuous


Parts Of Speech


Nouns

Countable and uncountable nouns

Verbal nouns

Singular and Plural nouns

Proper nouns

Nouns gender

Nouns definition

Concrete nouns

Abstract nouns

Common nouns

Collective nouns

Definition Of Nouns

Animate and Inanimate nouns

Nouns


Verbs

Stative and dynamic verbs

Finite and nonfinite verbs

To be verbs

Transitive and intransitive verbs

Auxiliary verbs

Modal verbs

Regular and irregular verbs

Action verbs

Verbs


Adverbs

Relative adverbs

Interrogative adverbs

Adverbs of time

Adverbs of place

Adverbs of reason

Adverbs of quantity

Adverbs of manner

Adverbs of frequency

Adverbs of affirmation

Adverbs


Adjectives

Quantitative adjective

Proper adjective

Possessive adjective

Numeral adjective

Interrogative adjective

Distributive adjective

Descriptive adjective

Demonstrative adjective


Pronouns

Subject pronoun

Relative pronoun

Reflexive pronoun

Reciprocal pronoun

Possessive pronoun

Personal pronoun

Interrogative pronoun

Indefinite pronoun

Emphatic pronoun

Distributive pronoun

Demonstrative pronoun

Pronouns


Pre Position


Preposition by function

Time preposition

Reason preposition

Possession preposition

Place preposition

Phrases preposition

Origin preposition

Measure preposition

Direction preposition

Contrast preposition

Agent preposition


Preposition by construction

Simple preposition

Phrase preposition

Double preposition

Compound preposition

prepositions


Conjunctions

Subordinating conjunction

Correlative conjunction

Coordinating conjunction

Conjunctive adverbs

conjunctions


Interjections

Express calling interjection

Phrases

Sentences


Grammar Rules

Passive and Active

Preference

Requests and offers

wishes

Be used to

Some and any

Could have done

Describing people

Giving advices

Possession

Comparative and superlative

Giving Reason

Making Suggestions

Apologizing

Forming questions

Since and for

Directions

Obligation

Adverbials

invitation

Articles

Imaginary condition

Zero conditional

First conditional

Second conditional

Third conditional

Reported speech

Demonstratives

Determiners


Linguistics

Phonetics

Phonology

Linguistics fields

Syntax

Morphology

Semantics

pragmatics

History

Writing

Grammar

Phonetics and Phonology

Semiotics


Reading Comprehension

Elementary

Intermediate

Advanced


Teaching Methods

Teaching Strategies

Assessment
Consonants
المؤلف:
Jan Tillery and Guy Bailey
المصدر:
A Handbook Of Varieties Of English Phonology
الجزء والصفحة:
333-18
2024-03-25
1087
Consonants
Although it is clearly most different from other American dialects in its vowel system, SAmE also includes some distinctive consonant features. Unlike many other varieties of American English, traditional SAmE preserved h before w in words like which and white, maintained j after alveolar stops and nasals in words like Tuesday, due, and news, and had unconstricted r in postvocalic position. However, over the last 120 years, and particularly since World War II, all of these have begun to disappear in the urban South. In initial clusters, h is now usually lost before w and sometimes before j, so that which is typically [wIʧ] and Houston sometimes 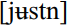 . Likewise, among younger Southern urbanites, j is generally lost after alveolars so that do and due are homophones (both are usually realized as
. Likewise, among younger Southern urbanites, j is generally lost after alveolars so that do and due are homophones (both are usually realized as 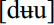 ).
).
The situation with r is somewhat more complicated. Although the Southern mountains and piney woods have always been rhotic, in the plantation areas of the South, earlier varieties of SAmE had unconstricted r in four environments:
(1) when r followed a vowel (as in fire, four, ford, and far),
(2) when it functioned as a stressed syllabic (as in first and fur),
(3) when it functioned as an unstressed syllabic (as in father), and
(4) occasionally when it occurred in intersyllabic position (as in MARY and MERRY).
Present-day urban SAmE, however, generally has constricted r in all of these environments. The expansion of constricted r began first in intersyllabic and stressed syllabic environments before World War II. Since that time constricted variants have become the norm in Southern metropolises not only in intersyllabic and stressed syllabic environments, but increasingly in postvocalic environments (after front vowels initially and then after back vowels) and in unstressed syllabic contexts as well. In fact, over the last quarter century, the expansion of rhotic variants has been so extensive among white Southerners that non-rhotic forms are now associated primarily with African Americans.
Three other features of traditional SAmE, however, have been preserved in urban SAmE to a greater extent. First, as in rural varieties, post-vocalic l is frequently vocalized; the vocalized l is often transcribed as [ɤ] in linguistic atlas records, but there is usually some lip rounding with vocalized l. Second, again as in rural varieties, medial z often undergoes assibilation before n so that isn’t is pronounced [Idn] and wasn’t pronounced [wΛdn] . (Note, however, that urban SAmE differs from rural varieties in that v is rarely assibilated in words like seven.) Finally, especially in rapid speech, final nasals are still sometimes realized only as vowel nasality; this accounts for the fact that don’t can be pronounced as [dõʊ]. Other consonant features of traditional SAmE phonology, such as intrusive t in words like once and the unusually high rate of consonant cluster simplification, have largely disappeared from urban SAmE.
 الاكثر قراءة في Phonology
الاكثر قراءة في Phonology
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















