
DNA Cloning : Vectors
 المؤلف:
Denise R. Ferrier
المؤلف:
Denise R. Ferrier
 المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry
المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry
 الجزء والصفحة:
الجزء والصفحة:
 2-1-2022
2-1-2022
 1534
1534
DNA Cloning : Vectors
Introduction of a foreign DNA molecule into a replicating cell permits the cloning or, amplification (that is, the production of many identical copies) of that DNA. [Note: Human DNA for cloning can be obtained from blood, saliva, and solid tissue.] In some cases, a single DNA fragment can be isolated and purified prior to cloning. More commonly, to clone a nucleotide sequence of interest, the total cellular DNA is first cleaved with a specific restriction enzyme, creating hundreds of thousands of fragments. Each of the resulting DNA fragments is joined to a DNA vector molecule (referred to as a cloning vector) to form a hybrid, or recombinant, DNA molecule. Each recombinant molecule carries its inserted DNA fragment into a single host cell (for example, a bacterium), where it is replicated. [Note: The process of introducing foreign DNA into a cell is called transformation for bacteria and yeast and transfection for higher eukaryotes.] As the host cell multiplies, it forms a clone in which every bacterium contains copies of the same inserted DNA fragment, hence the name “cloning.” The cloned DNA can be released from its vector by cleavage (using the appropriate restriction endonuclease) and isolated. By this mechanism, many identical copies of the DNA of interest can be produced. [Note: An alternative to amplification by biologic cloning, the polymerase chain reaction (PCR)]
Vectors
A vector is a molecule of DNA to which the fragment of DNA to be cloned is joined. Essential properties of a vector include the 1) capacity for autonomous replication within a host cell, 2) presence of at least one specific nucleotide sequence recognized by a restriction endonuclease, and 3) presence of at least one gene (such as an antibiotic resistance gene) that confers the ability to select for the vector. Commonly used vectors include plasmids and viruses.
1. Prokaryotic plasmids: Prokaryotic organisms typically contain single, large, circular chromosomes. In addition, most species of bacteria also normally contain small, circular, extrachromosomal DNA molecules called plasmids (Fig. 1). Plasmid DNA undergoes replication that may or may not be synchronized to chromosomal division. Plasmids may carry genes that convey antibiotic resistance to the host bacterium and may facilitate the transfer of genetic information from one bacterium to another. They can be readily isolated from bacterial cells, their circular DNA cleaved at specific sites by restriction endonucleases, and up to 15 kb (kilobases) of foreign DNA (cut with the same restriction enzyme) inserted. The recombinant plasmid vector can be introduced into a bacterium, producing large numbers of copies of the plasmid. The bacteria are grown in the presence of antibiotics, thus selecting for cells containing the hybrid plasmids, which provide antibiotic resistance (Fig.2). Artificial plasmids are routinely constructed. An example is the classic pBR322 (see Fig. 1), which contains an origin of replication, two antibiotic resistance genes, and >40 unique restriction sites. Use of plasmids is limited by the size of the DNA that can be inserted.

Figure 1: A partial map of pBR322 indicating the positions of its antibiotic resistance genes and 6 of the >40 unique sites recognized by specific restriction endonucleases. p = plasmid.
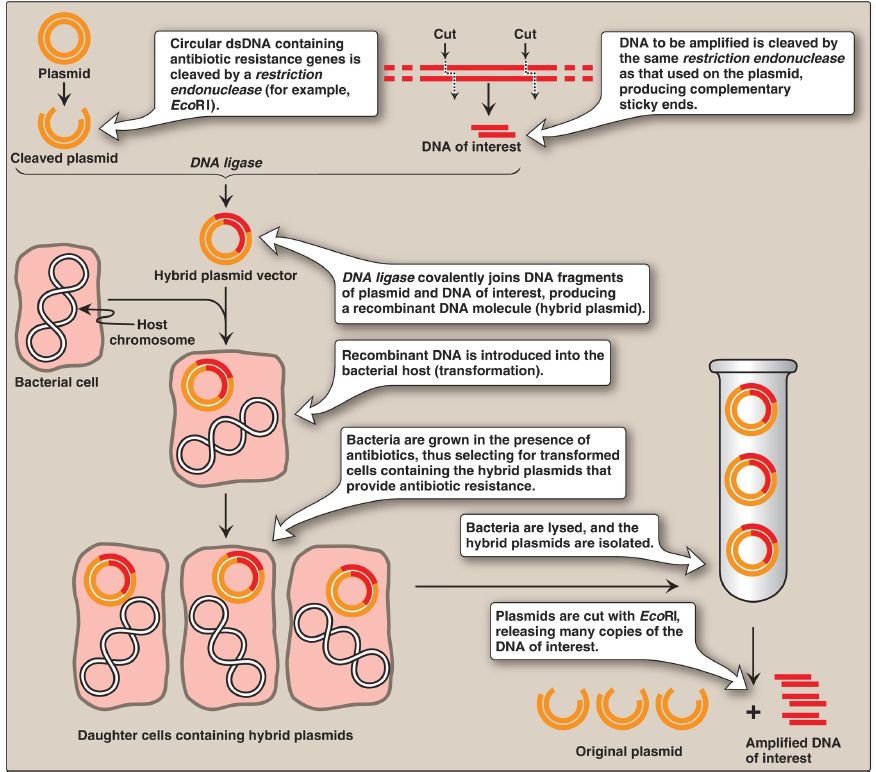
Figure 2: Summary of biologic gene cloning. [Note: Transformation is inefficient in that only a small percentage of the cells will contain the recombinant plasmid.] dsDNA = double-stranded DNA.
2. Other vectors: The development of improved vectors that can more efficiently accommodate larger DNA segments, or express the passenger genes in different cell types, has aided molecular genetics research and therapeutics. In addition to the prokaryotic plasmids described above, naturally occurring viruses that infect bacteria (bacteriophage λ, for example) or mammalian cells (retroviruses, for example), as well as artificial constructs such as cosmids and bacterial or yeast artificial chromosomes (BAC or YAC, respectively), are currently used as cloning vectors. [Note: BAC and YAC can accept DNA inserts of 100–300 kb and 250–1,000 kb, respectively.]
 الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحيوية
الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحيوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


