
Adipose Tissue: Energy Storage Depot
 المؤلف:
Denise R. Ferrier
المؤلف:
Denise R. Ferrier
 المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry
المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry
 الجزء والصفحة:
الجزء والصفحة:
 24-11-2021
24-11-2021
 1684
1684
Adipose Tissue: Energy Storage Depot
Adipose tissue is second only to the liver in its ability to distribute fuel molecules. In a 70-kg man, white adipose tissue (WAT) weighs ~14 kg, or about half as much as the total muscle mass. Nearly the entire volume of each adipocyte in WAT can be occupied by a droplet of anhydrous, calorically dense TAG (Fig. 1).
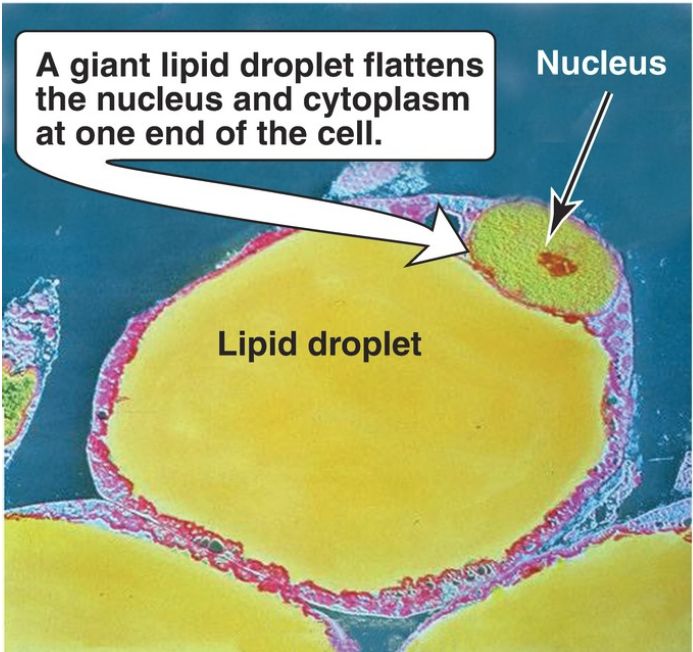
Figure 1: Colorized transmission electron micrograph of adipocytes.
A. Carbohydrate metabolism
1. Increased glucose transport: Circulating insulin levels are elevated in the absorptive state, resulting in an influx of glucose into adipocytes via insulin-sensitive GLUT-4 recruited to the cell surface from intracellular vesicles (Fig. 2, ). The glucose is phosphorylated by hexokinase.
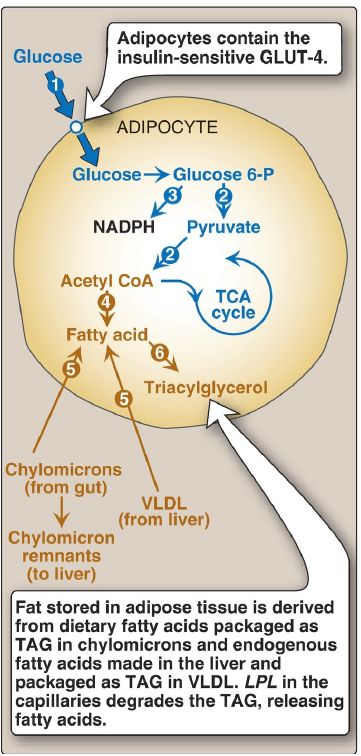
Figure 2: Major metabolic pathways in adipose tissue in the absorptive state. [Note: The numbers in the circles, which appear both in the figure and in the corresponding text, indicate important pathways for adipose tissue metabolism.] GLUT = glucose transporter; P = phosphate; NADPH = nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; CoA = coenzyme A; TCA = tricarboxylic acid; TAG = triacylglycerol; VLDL = very-low-density lipoprotein; LPL = lipoprotein lipase.
2. Increased glycolysis: The increased intracellular availability of glucose results in an enhanced rate of glycolysis (see Fig. 2, ). In adipose tissue, glycolysis serves a synthetic function by supplying glycerol 3-phosphate for TAG synthesis . [Note: Adipose tissue lacks glycerol kinase.]
3. Increased pentose phosphate pathway activity: Adipose tissue can metabolize glucose by means of the pentose phosphate pathway, thereby producing NADPH, which is essential for FA synthesis ( Fig. 2, ). However, in humans, de novo synthesis is not a major source of FA in adipose tissue, except when refeeding a previously fasted individual (see Fig. 2, ).
B. Fat metabolism
Most of the FA added to the TAG stores of adipocytes after consumption of a lipid-containing meal are provided by the degradation of exogenous (dietary) TAG in chylomicrons sent out by the intestine and endogenous TAG in VLDL sent out by the liver (see Fig. 2, ). The FA are released from the lipoproteins by lipoprotein lipase (LPL), an extracellular enzyme attached to the endothelial cells of capillary walls in many tissues, particularly adipose and muscle . In adipose tissue, LPL is upregulated by insulin. Thus, in the fed state, elevated levels of glucose and insulin favor storage of TAG (see Fig. 2, ), all the carbons of which are supplied by glucose. [Note: Elevated insulin favors the dephosphorylated (inactive) form of HSL , thereby inhibiting lipolysis in the wellfed state.]
 الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحيوية
الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحيوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


