


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 6-11-2015
Date: 2025-02-16
Date: 2025-01-13
|
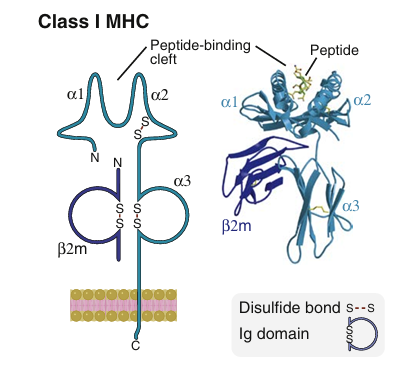
Each class I MHC molecule consists of an α chain noncovalently associated with a protein called β2-microglobulin that is encoded by a gene outside the MHC. The α chain consists of three extracellular domains followed by transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains.
• The amino-terminal αl and α2 domains of the α chain form two walls and a peptide-binding cleft, or groove, that can accommodate peptides typically 8 to 9 amino acids long. The floor of the peptide-binding cleft contains amino acid residues that bind peptides for display to T lymphocytes, and the tops of the cleft
walls make contact with the T cell receptor (which also contacts part of the displayed peptide) . The polymorphic residues of class I molecules—that is, the amino acids that differ among different individuals' MHC molecules are located in the αl and α2 domains of the α chain. Most of these polymorphic residues contribute to variations in the floor of the peptide-binding cleft and thus influence the ability of different MHC molecules to bind distinct sets of peptides.
The α3 domain is invariant and contains a site that binds the CD8 T cell coreceptor but not CD4., T cell activation requires recognition of MHC-associated peptide antigen by the TCR and simultaneous recognition of the MHC molecule by the coreceptor. Therefore, CD8+ T cells can only respond to peptides displayed by class I MHC molecules, the MHC molecules to which the CD8 coreceptor binds.



|
|
|
|
للعاملين في الليل.. حيلة صحية تجنبكم خطر هذا النوع من العمل
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
"ناسا" تحتفي برائد الفضاء السوفياتي يوري غاغارين
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
نحو شراكة وطنية متكاملة.. الأمين العام للعتبة الحسينية يبحث مع وكيل وزارة الخارجية آفاق التعاون المؤسسي
|
|
|