


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 12-7-2020
Date: 23-11-2020
Date: 28-7-2020
|
X-ray astronomy: X-ray energies
X-ray energy emitted by celestial sources is totally absorbed by the Earth’s atmosphere and observations can only be made by special equipment launched by rockets. The first detections of cosmic x-rays were made from rocket flights in the early 1960s. Since then, there have been several satellite platforms carrying x-ray instruments for survey work and spectrometry with progress being made both in terms of sensitivity and spatial resolution.
In the spectral range of wavelengths shorter than the ultraviolet, it is usual to describe the radiation in terms of the photon energy rather than its wavelength or frequency, the unit being the electron volt. In the optical region, photon energies are typically of the order of 2 eV, while x-ray photons have energies of the order of a few keV. This can be checked by considering the wavelength (frequency) to photon energy conversion as follows.
In the optical region λ ∼ 500 nm (5000 A˚ ) so that
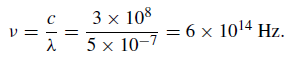
The energy of a photon is hν and for the optical region its value is
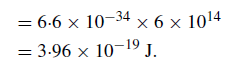
Converting the energy units from joules to electron volts gives a photon energy of
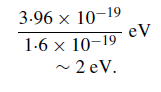
For x-rays, it has already been mentioned that the energies are a few keV and higher and the reverse calculation shows that wavelengths of ∼0·5 nm or 5 ˚A are covered. With such extremely short wavelengths, it will be readily appreciated that the principles used for optical telescopes cannot be extended to x-rays.



|
|
|
|
للعاملين في الليل.. حيلة صحية تجنبكم خطر هذا النوع من العمل
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
"ناسا" تحتفي برائد الفضاء السوفياتي يوري غاغارين
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
نحو شراكة وطنية متكاملة.. الأمين العام للعتبة الحسينية يبحث مع وكيل وزارة الخارجية آفاق التعاون المؤسسي
|
|
|